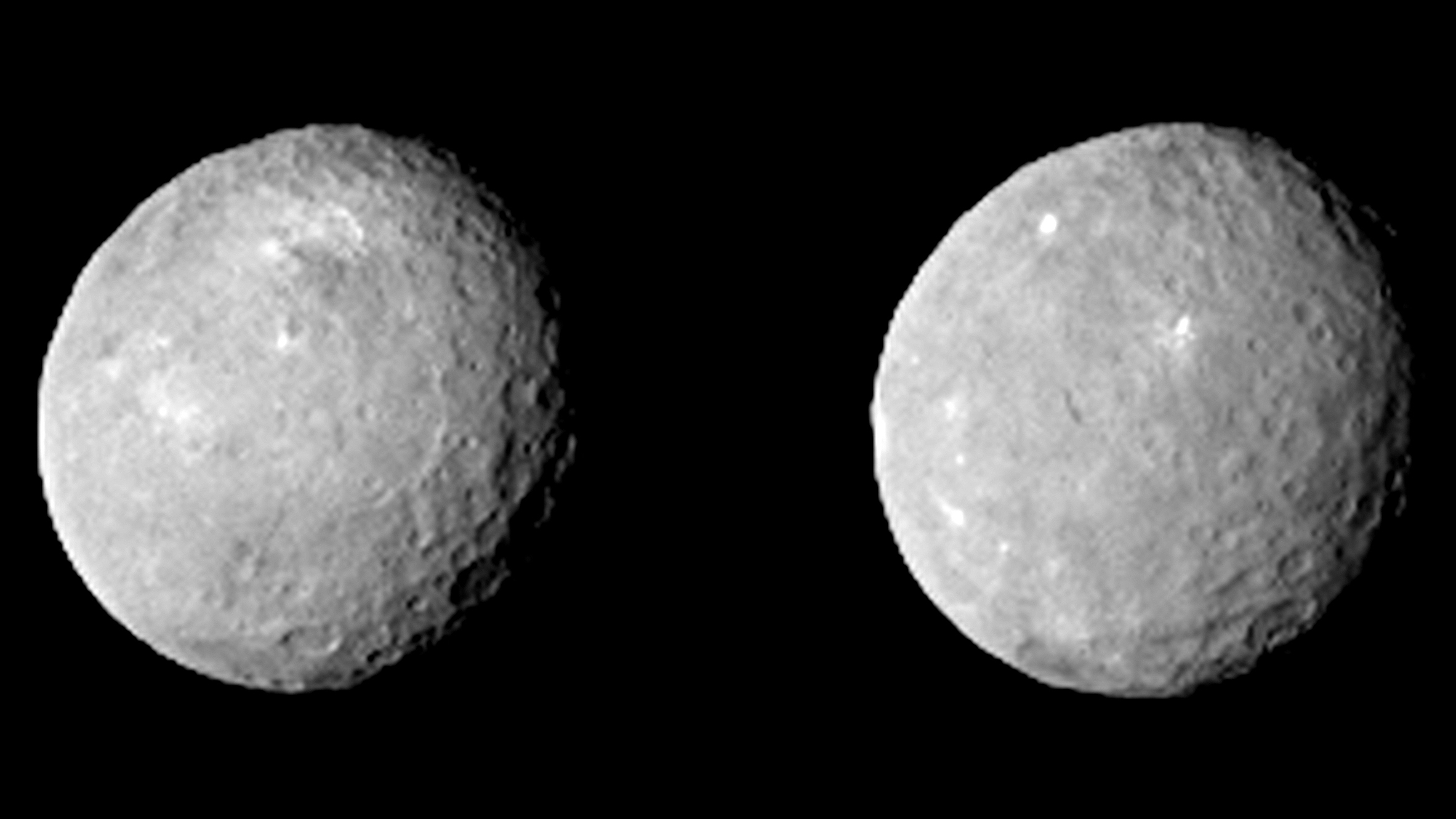
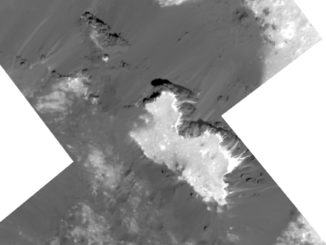
Images from NASA’s Dawn spacecraft on approach to the dwarf planet Ceres show a world pockmarked by craters and mysterious bright spots, and scientists are eager for a better look in the weeks ahead.
The latest images were taken Feb. 12 at a distance of 52,000 miles, or 83,000 kilometers, from Ceres. NASA released the fresh views Tuesday.
Every picture taken of Ceres in the coming weeks will show greater detail, as Dawn is set to be captured by the Texas-sized world’s gravity March 6. The dwarf planet will pull Dawn into the first of a series of survey orbits 8,400 miles from Ceres around April 23.
The imagery so far reveals Ceres as a cratered world, and Dawn will make a global map of the dwarf planet during its time in orbit.
But several bright spots have captured the attention of scientists.
“As we slowly approach the stage, our eyes transfixed on Ceres and her planetary dance, we find she has beguiled us but left us none the wiser,” said Chris Russell, principal investigator of the Dawn mission, based at UCLA. “We expected to be surprised; we did not expect to be this puzzled.”
The suspense is compounded by Dawn’s slow rate of approach. The probe’s ion propulsion system is gradually nudging Dawn on a trajectory closer to Ceres, eventually moving the spacecraft close enough to be grasped by the 590-mile diameter dwarf planet’s gravity.
“I want to know what is causing the bright spots,” Russell wrote in an email to Spaceflight Now. “The increased resolution seems to have moved us no closer to answering this mystery. I am frustrated by the suspense. This is the one problem of ion propulsion: We are closing in on Ceres very slowly.”
The latest photos have a resolution have 4.9 miles, or 7.8 kilometers, per pixel, according to a NASA press release.
Dawn’s framing camera will take its next set of images Feb. 20 at a range of about 30,000 miles. After late February, the resolution of Dawn’s imagery will be reduced as the spacecraft passes Ceres and flies in front of it, before being pulled closer in early April for insertion into orbit.
Soon after arriving in April, the spacecraft’s instruments will look for the signature of water vapor plumes shooting into space from the surface of Ceres, which may be blanketed in a crust of ice.
Dawn will orbit closest to Ceres in December at an altitude of 232 miles.
Dawn’s mission planners say the spacecraft could operate around Ceres until late 2016.
Ceres is the second destination for NASA’s Dawn mission, which launched in September 2007 and visited asteroid Vesta in 2011 and 2012.
Follow Stephen Clark on Twitter: @StephenClark1.