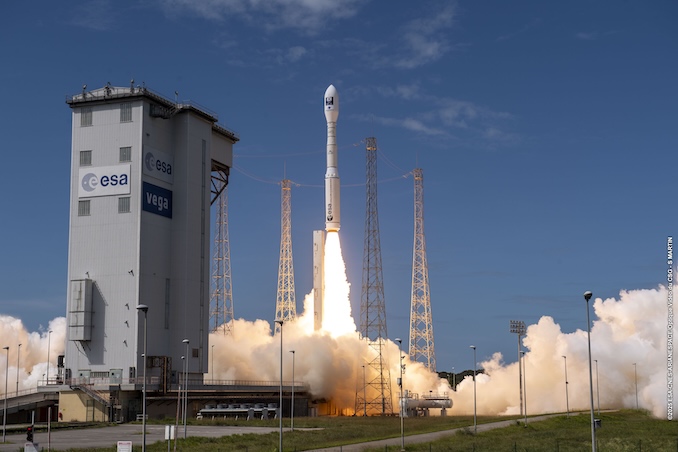
South Korea’s latest Earth observation satellite was delivered into a Sun-synchronous orbit Monday afternoon following a launch onboard a Vega-C rocket by Arianespace.
The KOrea Multi-Purpose SATellite-7 (KOMPSAT-7) mission launched from Europe’s Spaceport. The 35-meter-tall (115 ft) rocket zipped away from the pad under the power of a P120C solid rocket motor.
About 44 minutes after liftoff, the KOMPSAT-7 satellite was deployed into SSO an altitude of 576 km.
“By launching the KOMPSAT-7 satellite, set to significantly enhance South Korea’s Earth observation capabilities, Arianespace is proud to support an ambitious national space program,” said David Cavaillolès, CEO of Arianespace, in a statement. “This mission marks the fourth satellite Arianespace has launched for the Korea Aerospace Research Institute.”
About an hour and nine minutes after it separated from the fourth stage of the Vega-C rocket, the Korea Aerospace Research Institute (KARI) confirmed that teams were able to successfully make contact with the satellite through the Troll Satellite Station in Antarctica.
KARI said the KOMPSAT-7 satellite is designed as the successor to KOMPSAT-3A, which launched on a Soviet-era ballistic missile, Dnepr, in March 2015. This new spacecraft features what KARI calls its Advanced Earth Imaging Sensor System – High Resolution (AEISS-HR) payload alongside a control management gyroscope for maneuvering.
“To maximize the effectiveness of its ultra-high-resolution optical payload, KOMPSAT-7 incorporates a CMG for enhanced agility—a first among Korean satellites—and features an onboard computer that is over three times faster than those used in KOMPSAT-3 and 3A, significantly improving attitude control performance,” according to KARI’s website.
“The ground image processing system applies advanced parallel processing techniques, enabling it to complete first-stage geometric correction and generate imagery within 15 minutes after receiving satellite data.”
KARI said in a post on Facebook following the launch that the KOMPSAT-7 satellite is anticipated to begin providing ground observation images sometime in the first half of 2026.
Monday’s flight was the sixth launch of a Vega-C rocket to date and the sixth launch by Arianespace in 2025.
[아리랑 7호, 발사 성공]
12월 2일 02:21, 프랑스령 기아나우주센터에서 아리랑 7호가 성공적으로 발사되었습니다.VEGA-C로부터 정상 분리되었고, 남극 트롤 지상국과 첫 교신에도 성공했습니다. 초기 상태와 목표궤도 안착이 확인되었으며, 2026년 상반기부터 지상관측영상을 제공할 예정입니다. pic.twitter.com/E3KOgUTTLq
— 한국항공우주연구원 (@kari2030) December 2, 2025