STORY WRITTEN FOR CBS NEWS & USED WITH PERMISSION
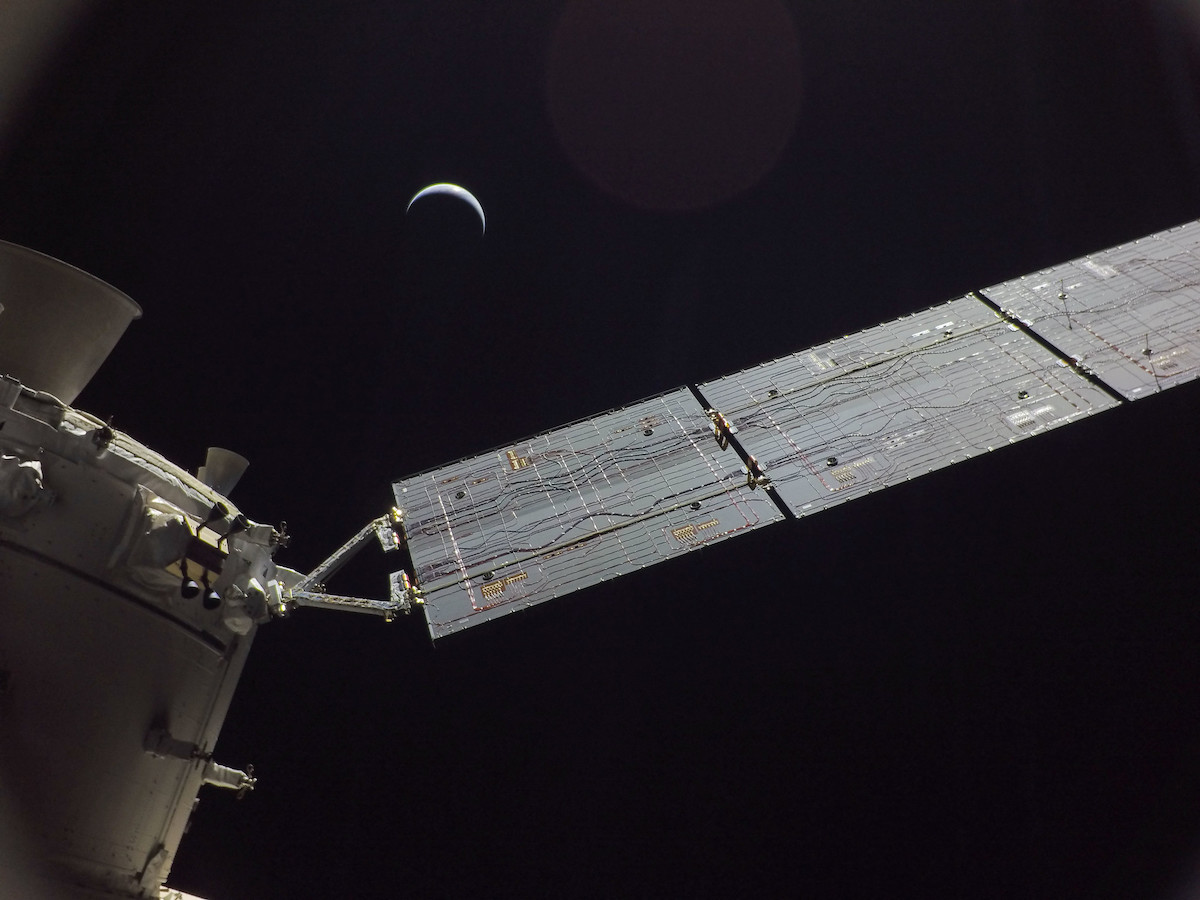

Closing out a 25-day voyage around the moon, NASA’s Artemis 1 spacecraft closed in on Earth Saturday, on track for a 25,000-mph re-entry Sunday that will subject the unpiloted capsule to a hellish 5,000-degree inferno before splashdown off Baja California.
In an unexpected but richly-symbolic coincidence, the end of the Artemis 1 mission, expected at 12:39 p.m., will come 50 years to the day after the final Apollo moon landing in 1972.
Testing the Orion capsule’s 16.5-foot-wide Apollo-derived Avcoat heat shield is the top priority of the Artemis 1 mission, “and it is our priority-one objective for a reason,” said mission manager Mike Sarafin.
“There is no arc jet or aerothermal facility here on Earth capable of replicating hypersonic reentry with a heat shield of this size,” he said. “And it is a brand new heat shield design, and it is a safety-critical piece of equipment. It is designed to protect the spacecraft and (future astronauts) … so the heat shield needs to work.”
Launched November 16 on the maiden flight of NASA’s huge new Space Launch System rocket, the unpiloted Orion capsule was propelled out of Earth orbit and on to the moon for an exhaustive series of tests, putting its propulsion, navigation, power and computer systems through their paces in the deep space environment.
While flight controllers ran into still-unexplained glitches with its power system, initial “funnies” with its star trackers and degraded performance from a phased array antenna, the Orion spacecraft and its European Space Agency-built service module worked well overall, achieving virtually all of their major objectives to this point.
“We’ve collected an immense amount of data characterizing system performance from the power system, the propulsion, GNC (guidance, navigation and control) and so far, the flight control team has downlinked to over 140 gigabytes of engineering and imagery data,” said Jim Geffre, the Orion vehicle integration manager.
The team is already analyzing that data “to help not only understand the performance on Artemis 1, but play forward for all subsequent missions,” he said.
If all goes well, NASA plans to follow the Artemis 1 mission by sending four astronauts around the moon in the program’s second flight — Artemis 2 — in 2024. The first moon landing would follow in the 2025-26 timeframe when NASA says the first woman and the next man will set foot on the lunar surface.
The unpiloted Artemis 1 capsule flew through half of an orbit around the moon that carried it farther from Earth — 268,563 miles — than any previous human-rated spacecraft. Two critical firings of its main engine set up a low-altitude lunar flyby last Monday that, in turn, put the craft on course for splashdown Sunday.
NASA originally planned to bring the ship down west of San Diego, but a predicted cold front bringing higher winds and rougher seas prompted mission managers to move the landing site south by about 350 miles. Splashdown is now expected south of Guadalupe Island some 200 miles west of Baja California.
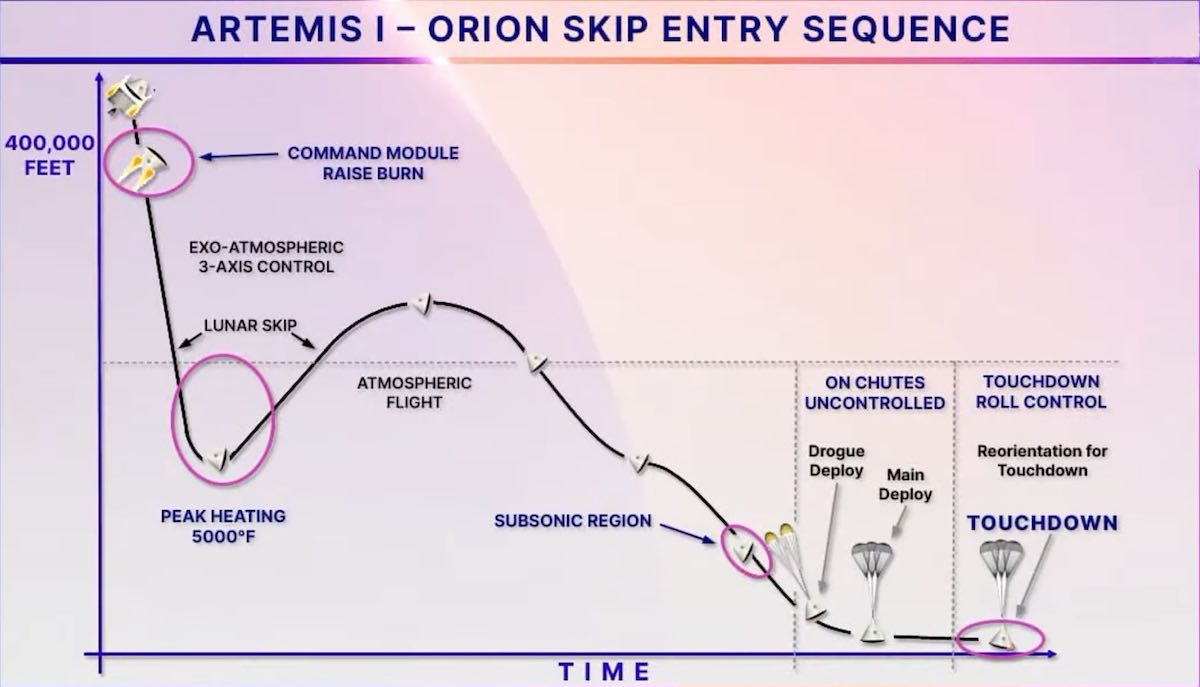
Approaching from nearly due south, the Orion spacecraft, traveling at 32 times the speed of sound, is expected to slam back into the discernible atmosphere at an altitude of 400,000 feet, or about 76 miles, at 12:20 p.m.
NASA planners devised a unique “skip-entry” profile that will cause Orion skip across the top of the atmosphere like a flat stone skipping across calm water. Orion will plunge from 400,000 feet to about 200,000 feet in just two minutes, then climb back up to about 295,000 feet before resuming its computer-guided fall to Earth.
Within a minute and a half of entry, atmospheric friction will generate temperatures across the heat shield reaching nearly 5,000 degrees Fahrenheit, enveloping the spacecraft in an electrically charged plasma that will block communications with flight controllers for about five minutes.
After another two-and-a-half minute communications blackout during its second drop into the lower atmosphere, the spacecraft will continue decelerating as it closes in on the targeted landing site, slowing to around 650 mph, roughly the speed of sound, about 15 minutes after the entry began.
Finally, at an altitude of about 22,000 feet and a velocity of around 280 mph, small drogue parachutes will deploy to stabilize the spacecraft. The ship’s main parachutes will deploy at an altitude of about 5,000 feet, slowing Orion to a sedate 18 mph or so for splashdown at 12:39 p.m.
Expected mission duration: 25 days 10 hours 52 minutes, covering 1.4 million miles since blastoff November 16.
NASA and Navy recovery crews aboard the USS Portland, an amphibious dock vessel, will be standing by within sight of splashdown, ready to secure the craft and tow it into the Navy ship’s flooded “well deck.”
Once the deck’s gates are closed, the water will be pumped out, leaving Orion on a custom stand, protecting its heat shield, for the trip back to Naval Base San Diego.
But first, the recovery team will stand by for up to two hours while engineers collect data on how the heat of re-entry soaked into the spacecraft and what effects, if any, that might have on the crew cabin temperature.
“We are on track to have a fully successful mission with some bonus objectives that we’ve achieved along the way,” Sarafin said. “And on entry day, we will realize our priority one objective, which is to demonstrate the vehicle at lunar re-entry conditions.”
