
Spaceflight Now +

|

|

|

|

Premium video content for our Spaceflight Now Plus subscribers.

Space shuttle update
 Space shuttle program officials Friday held a news conference at the Johnson Space Center to provide a status report on efforts to understand and fix the external tank foam insulation problems and confirm that the next launch won't happen before May 2006. Space shuttle program officials Friday held a news conference at the Johnson Space Center to provide a status report on efforts to understand and fix the external tank foam insulation problems and confirm that the next launch won't happen before May 2006.

 Dial-up | Broadband Dial-up | Broadband

Saturn's spongy moon
 Stunning images of Saturn's moon Hyperion taken by the Cassini spacecraft show a surface dotted with craters and modified by some process, not yet understood, to create a strange, "spongy" appearance, unlike the surface of any other moon around the ringed planet. Stunning images of Saturn's moon Hyperion taken by the Cassini spacecraft show a surface dotted with craters and modified by some process, not yet understood, to create a strange, "spongy" appearance, unlike the surface of any other moon around the ringed planet.

 Play video Play video

ISS crew back on Earth
 Russian recovery forces pull the space travelers from the just-landed Soyuz capsule as dawn begins to break over the touchdown site in north-central Kazakhstan. Russian recovery forces pull the space travelers from the just-landed Soyuz capsule as dawn begins to break over the touchdown site in north-central Kazakhstan.

 Play video Play video

Astronaut parade
 The astronauts from space shuttle Discovery's return to flight mission recently paid a visit to Japan, the homeland of mission specialist Souichi Noguchi, and were treated to a grand parade. The astronauts from space shuttle Discovery's return to flight mission recently paid a visit to Japan, the homeland of mission specialist Souichi Noguchi, and were treated to a grand parade.

 Play video Play video

ISS command change
 The International Space Station's outgoing Expedition 11 crew and the new Expedition 12 crew gather inside the Destiny laboratory module for a change of a command ceremony, complete with ringing of the outpost's bell, as the human presence in space continues. The International Space Station's outgoing Expedition 11 crew and the new Expedition 12 crew gather inside the Destiny laboratory module for a change of a command ceremony, complete with ringing of the outpost's bell, as the human presence in space continues.

 Play video Play video

Expedition 11 in review
 The Expedition 11 mission of commander Sergei Krikalev and flight engineer John Phillips aboard the International Space Station is winding down, and this narrated retrospective looks back at the key events of the half-year voyage in orbit. The Expedition 11 mission of commander Sergei Krikalev and flight engineer John Phillips aboard the International Space Station is winding down, and this narrated retrospective looks back at the key events of the half-year voyage in orbit.

 Play video Play video

Pluto spacecraft
 The Pluto New Horizons spacecraft, destined to become the first robotic probe to visit Pluto and its moon Charon, arrives at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in advance of its January blastoff. The Pluto New Horizons spacecraft, destined to become the first robotic probe to visit Pluto and its moon Charon, arrives at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in advance of its January blastoff.

 Play video Play video

Life on the station
 NASA astronauts Bill McArthur and John Phillips chat with Associated Press space reporter Marcia Dunn about life aboard the International Space Station in this live space-to-Earth interview from the Destiny laboratory module on October 5. NASA astronauts Bill McArthur and John Phillips chat with Associated Press space reporter Marcia Dunn about life aboard the International Space Station in this live space-to-Earth interview from the Destiny laboratory module on October 5.

 Dial-up | Broadband Dial-up | Broadband

West Coast Delta 4
 In preparation for the West Coast launch of Boeing's next-generation Delta 4 rocket, the two-stage vehicle is rolled out of its horizontal hangar and driven to the Space Launch Complex-6 pad for erection. The nose cone for the NRO payload is then brought to the pad. In preparation for the West Coast launch of Boeing's next-generation Delta 4 rocket, the two-stage vehicle is rolled out of its horizontal hangar and driven to the Space Launch Complex-6 pad for erection. The nose cone for the NRO payload is then brought to the pad.

 Play video Play video

West Coast shuttle
 Boeing's Delta 4 rocket pad at Vandenberg Air Force Base was renovated in recent years, transforming Space Launch Complex-6 from the West Coast space shuttle launch site into a facility for the next-generation unmanned booster. This collection of footage shows the 1985 launch pad test using NASA's orbiter Enterprise. Boeing's Delta 4 rocket pad at Vandenberg Air Force Base was renovated in recent years, transforming Space Launch Complex-6 from the West Coast space shuttle launch site into a facility for the next-generation unmanned booster. This collection of footage shows the 1985 launch pad test using NASA's orbiter Enterprise.

 Full coverage Full coverage

 Become a subscriber Become a subscriber
 More video More video

|

|

|

|
|

|

Hubble examines the moon in search for resources
NASA NEWS RELEASE
Posted: October 19, 2005
NASA is using the unique capabilities of the Hubble Space Telescope for a new class of scientific observations of the Earth's moon.

Hubble imaged Aristarchus crater and nearby Schroter's Valley rille on Aug. 21, 2005. The Hubble images reveal fine-scale details of the crater's interior and exterior in ultraviolet and visible wavelengths at a scale of approximately 165 to 330 feet (50 to 100 meters) per picture element. Credit: NASA, ESA and J. Garvin (NASA/GSFC)
Download larger image version here
|
Hubble's resolution and sensitivity to ultraviolet light have allowed the telescope to search for important oxygen-bearing minerals on the moon. Since the moon does not have a breathable atmosphere, minerals, such as ilmenite (titanium and iron oxide), may be critical for a sustained human lunar presence. Ilmenite is a potential source of oxygen for breathing or to power rockets.
The new Hubble observations are the first high-resolution, ultraviolet images ever acquired of the moon. The images provide scientists with a new tool to study mineral variations within the lunar crust. As NASA plans future expeditions to the moon, such data, in combination with other measurements, will help ensure the most valuable sites are targeted for robotic and human missions.
"These observations of the moon have been a challenging and highly successful technological achievement for NASA and the Hubble team, since the telescope was not originally designed for lunar observations," said Jennifer Wiseman, program scientist for the Hubble at NASA Headquarters. "The images will inform both scientific studies of lunar geology and future decisions on further lunar exploration," she said.
Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys snapped ultraviolet and visible light images of known geologically diverse areas on the side of the moon nearest Earth. These included the Aristarchus impact crater and the adjacent Schroter's Valley. Hubble also photographed the Apollo 15 and 17 landing sites, where astronauts collected rock and soil samples in 1971 and 1972.
Scientists are comparing the properties of the rock and soil samples from the Apollo sites with the new Hubble images, and the Aristarchus region, which neither humans nor robotic spacecraft have visited. The Hubble observations of Aristarchus crater and Schroter's Valley will help refine researchers' understanding of the diverse, scientifically interesting materials in the region and to unravel their full resource potential.
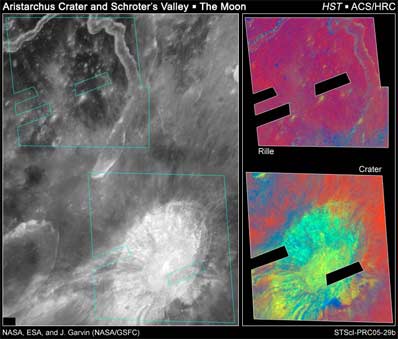
This view of the lunar impact crater Aristarchus and adjacent features (Herodotus crater, Schroter's Valley rille) illustrates the ultraviolet and visible wavelength characteristics of this geologically diverse region of the Moon. The two inset images illustrate one preliminary approach for isolating differences due to such effects as composition, soil maturity, mixing, and impact ejecta emplacement. Credit: NASA, ESA and J. Garvin (NASA/GSFC)
Download larger image version here
|
"Our initial findings support the potential existence of some unique varieties of oxygen-rich glassy soils in both the Aristarchus and Apollo 17 regions. They could be well-suited for visits by robots and human explorers in efforts to learn how to live off the land on the moon," said Jim Garvin, chief scientist at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md. Garvin is principal investigator for the project.
"While it will require many months before fully quantitative results can be developed, we already have evidence that these new observations will improve the precision by which we can understand materials such as ilmenite to help better inform exploration decisions," Garvin said.
Hubble's lunar observation analysis team included colleagues from Goddard and Cornell University, Ithaca, N.Y.; Brown University, Providence, R.I.; Northwestern University, Evanston, Ill.; the University of Pittsburgh.; and the University of Hawaii, Manoa.
The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. The Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore conducts Hubble science operations. It is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., Washington, under contract with Goddard.

Additional coverage for subscribers:
 VIDEO:
SCIENCE NEWS BRIEFING VIDEO:
SCIENCE NEWS BRIEFING
DIAL-UP 1 | DIAL-UP 2
BROADBAND 1 | BROADBAND 2
 SUBSCRIBE NOW SUBSCRIBE NOW

|

|

|

|


|



