
Spaceflight Now +

|

|

|

|

Premium video content for our Spaceflight Now Plus subscribers.

Titan up close
 Scientists reveal stunning pictures of Saturn's moon Titan and other results during this news conference from July 3. (38min 17sec file) Scientists reveal stunning pictures of Saturn's moon Titan and other results during this news conference from July 3. (38min 17sec file)
 Play video Play video

Saturn ring pictures
 Cassini's stunning close-up images of the rings around Saturn, taken just after the craft entered orbit Thursday morning, are presented with expert narration by Carolyn Porco, the mission imaging team leader. (8min 39sec file) Cassini's stunning close-up images of the rings around Saturn, taken just after the craft entered orbit Thursday morning, are presented with expert narration by Carolyn Porco, the mission imaging team leader. (8min 39sec file)
 Play video Play video

Burn ignition!
 Mission control erupts in applause as communications from Cassini confirm the orbit insertion burn has begun. (60sec file) Mission control erupts in applause as communications from Cassini confirm the orbit insertion burn has begun. (60sec file)
 Play video Play video

Burn completed
 Signals from Cassini announce the conclusion of the Saturn orbit insertion burn, confirming the spacecraft has arrived at the ringed planet. (2min 15sec file) Signals from Cassini announce the conclusion of the Saturn orbit insertion burn, confirming the spacecraft has arrived at the ringed planet. (2min 15sec file)
 Play video Play video

Post-arrival briefing
 Mission officials hold a post-orbit insertion burn news conference at 1 a.m. EDT July 1 to discuss Cassini's successful arrival at Saturn. (25min 27sec file) Mission officials hold a post-orbit insertion burn news conference at 1 a.m. EDT July 1 to discuss Cassini's successful arrival at Saturn. (25min 27sec file)
 Play video Play video

Wednesday's status briefing
 Cassini's health in the final hours before arrival at Saturn is presented in this status briefing from 12 p.m. EDT on June 30. (33min 09sec file) Cassini's health in the final hours before arrival at Saturn is presented in this status briefing from 12 p.m. EDT on June 30. (33min 09sec file)
 Play video Play video

International cooperation
 Officials from the U.S., European and Italian space agencies discuss the international cooperation in the Cassini mission and future exploration projects during this news conference from 2 p.m. EDT June 30. (19min 35sec file) Officials from the U.S., European and Italian space agencies discuss the international cooperation in the Cassini mission and future exploration projects during this news conference from 2 p.m. EDT June 30. (19min 35sec file)
 Play video Play video

'Ring-side' chat
 This informal "ring-side chat" from 5 p.m. EDT June 30 discusses the Cassini mission to Saturn and the future of space exploration. (49min 20sec file) This informal "ring-side chat" from 5 p.m. EDT June 30 discusses the Cassini mission to Saturn and the future of space exploration. (49min 20sec file)
 Play video Play video

Phoebe science briefing
 Scientists report scientific results from the Cassini spacecraft's close-up examination of Saturn's moon Phoebe. (31min 53sec file) Scientists report scientific results from the Cassini spacecraft's close-up examination of Saturn's moon Phoebe. (31min 53sec file)
 Play video Play video

Cassini preview
 The Cassini spacecraft's arrival at Saturn is previewed in this detailed news conference from NASA Headquarters on June 3. (50min 01sec file) The Cassini spacecraft's arrival at Saturn is previewed in this detailed news conference from NASA Headquarters on June 3. (50min 01sec file)
 Play video Play video

Cassini mission science
 The scientific objectives of the Cassini mission to study the planet Saturn, its rings and moons are explained by Charles Elachi, director of the Jet Propulsion Laboratory. (4min 54sec file) The scientific objectives of the Cassini mission to study the planet Saturn, its rings and moons are explained by Charles Elachi, director of the Jet Propulsion Laboratory. (4min 54sec file)
 Play video Play video

 Become a subscriber Become a subscriber
 More video More video

|

|

|

|

|

|

Ultraviolet pictures hint at origin of Saturn's rings
UNIVERSITY OF COLORADO NEWS RELEASE
Posted: July 7, 2004
The best view ever of Saturn's rings in the ultraviolet indicates there is more ice toward the outer part of the rings, hinting at ring origin and evolution, say two University of Colorado at Boulder researchers involved in the Cassini mission.
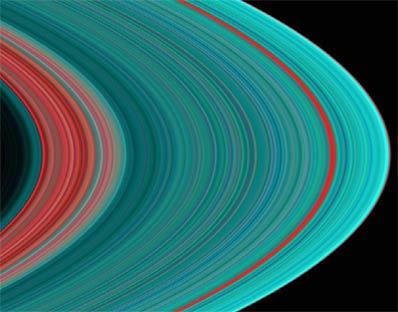
From the inside out, the "Cassini division" in faint red at left is followed by the A ring in its entirety. The A ring begins with a "dirty" interior of red followed by a general pattern of more turquoise as it spreads away from the planet, which indicates denser material made up of ice. The red band roughly three-fourths of the way outward in the A ring is known as the Encke gap.
Download a larger image version here
|
Researchers from CU-Boulder's Laboratory for Atmospheric and
Space Physics, Joshua Colwell and Larry Esposito, said the UV spectra
taken during the Cassini spacecraft's orbital insertion June 30 show
definite compositional variation in the A, B and C rings.
Esposito, who discovered the F ring around Saturn in 1979
using Pioneer 11 data, is the team leader for Cassini's Ultraviolet
Imaging Spectrograph, or UVIS, a $12.5 million instrument riding on
the spacecraft. A UVIS team member and ring expert, Colwell created
the color-enhanced images from the spectra.
The CU-Boulder built UVIS instrument is capable of resolving
the rings to show features up to 60 miles across, roughly 10 times
the resolution obtained by the Voyager 2 spacecraft. The instrument
was able to resolve the "Cassini division," discovered by Giovanni
Domenico Cassini in the 17th century, which separates the A and B
rings of Saturn, proving the rings are not one contiguous feature.
The ring system begins from the inside out with the D, C, B
and A rings followed by the F, G and E rings. The red in both images
indicates sparser ringlets likely made of "dirty," and possibly
smaller, particles than in the denser, icier turquoise ringlets.
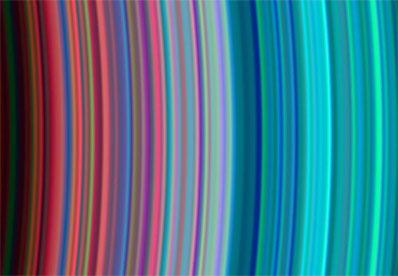
This image shows the outer C and inner B rings respectively from left to right, with the inner B ring beginning a little more than halfway across the image. The general pattern is from "dirty" red particles to the denser ice shown in turquoise as the ringlets spread outward.
Download a larger image version here
|

Additional coverage for subscribers:
 VIDEO:
WATCH SATURDAY'S NEWS CONFERENCE ON TITAN PICTURES QT VIDEO:
WATCH SATURDAY'S NEWS CONFERENCE ON TITAN PICTURES QT
 VIDEO:
WATCH FRIDAY'S SCIENCE NEWS CONFERENCE QT VIDEO:
WATCH FRIDAY'S SCIENCE NEWS CONFERENCE QT

 VIDEO:
THURSDAY'S NEWS BRIEFING ON CASSINI'S FIRST PICTURES QT VIDEO:
THURSDAY'S NEWS BRIEFING ON CASSINI'S FIRST PICTURES QT
 VIDEO:
RING PICTURES ARE PRESENTED WITH EXPERT NARRATION QT VIDEO:
RING PICTURES ARE PRESENTED WITH EXPERT NARRATION QT
 VIDEO:
CASSINI RE-DISCOVERS TINY MOONS ATLAS AND PAN QT VIDEO:
CASSINI RE-DISCOVERS TINY MOONS ATLAS AND PAN QT
 VIDEO:
CASSINI BOOMING SOUNDS FROM BOW-SHOCK CROSSING QT VIDEO:
CASSINI BOOMING SOUNDS FROM BOW-SHOCK CROSSING QT

 VIDEO:
CASSINI BEGINS ENGINE FIRING TO ENTER ORBIT QT VIDEO:
CASSINI BEGINS ENGINE FIRING TO ENTER ORBIT QT
 VIDEO:
BURN ENDS SUCCESSFULLY TO PUT CASSINI IN ORBIT QT VIDEO:
BURN ENDS SUCCESSFULLY TO PUT CASSINI IN ORBIT QT
 VIDEO:
POST-ARRIVAL NEWS CONFERENCE QT VIDEO:
POST-ARRIVAL NEWS CONFERENCE QT

 VIDEO:
WEDNESDAY'S 12 P.M. EDT CASSINI STATUS BRIEFING QT VIDEO:
WEDNESDAY'S 12 P.M. EDT CASSINI STATUS BRIEFING QT
 VIDEO:
A LOOK AT INTERNATIONAL COOPERATION QT VIDEO:
A LOOK AT INTERNATIONAL COOPERATION QT
 VIDEO:
'RING-SIDE CHAT' ABOUT SPACE EXPLORATION QT VIDEO:
'RING-SIDE CHAT' ABOUT SPACE EXPLORATION QT
 VIDEO:
AN OVERVIEW OF CASSINI'S RADIO SCIENCE QT VIDEO:
AN OVERVIEW OF CASSINI'S RADIO SCIENCE QT

 VIDEO:
TUESDAY'S CASSINI MISSION OVERVIEW BRIEFING QT VIDEO:
TUESDAY'S CASSINI MISSION OVERVIEW BRIEFING QT
 VIDEO:
CASSINI'S ARRIVAL AT SATURN EXPLAINED QT VIDEO:
CASSINI'S ARRIVAL AT SATURN EXPLAINED QT
 VIDEO:
SCIENCE OBJECTIVES FOR CASSINI ORBITER QT VIDEO:
SCIENCE OBJECTIVES FOR CASSINI ORBITER QT
 VIDEO:
HUYGENS LANDER SCIENCE OBJECTIVES QT VIDEO:
HUYGENS LANDER SCIENCE OBJECTIVES QT
 SUBSCRIBE NOW SUBSCRIBE NOW

|

|

|

|

|



